1. Introduction: The First Major Retailer to Buckle Under Tariff Pressures
On April 2, 2025, former U.S. President Donald Trump reignited the U.S.-China trade war by imposing steep tariffs on Chinese goods. Within weeks, Walmart—the world’s largest retailer—became the first major U.S. company to falter under the strain.
Despite initially demanding Chinese suppliers absorb the costs, Walmart reversed course just 20 days later, announcing it would shoulder all tariffs to avoid empty shelves and customer backlash. This abrupt shift revealed critical weaknesses in U.S. supply chains and the harsh realities of decoupling from China.
 Walmart’s struggle to maintain inventory during the tariff crisis highlighted the fragility of global supply chains.
Walmart’s struggle to maintain inventory during the tariff crisis highlighted the fragility of global supply chains.
2. Timeline of Walmart’s Tariff Crisis
A. Trump’s Tariff Escalation
- February 2025: Trump proposed a 20% tariff on Chinese imports, set to take effect on April 2.
- April 8, 2025: Tariffs on Chinese goods surged to 145%, far exceeding initial estimates.
B. Walmart’s Initial Ultimatum
- March 11, 2025: Walmart issued a stern notice to Chinese suppliers, demanding they absorb all tariff costs or face halted orders. The move sparked protests and intervention by China’s Ministry of Commerce.
C. The 20-Day Collapse
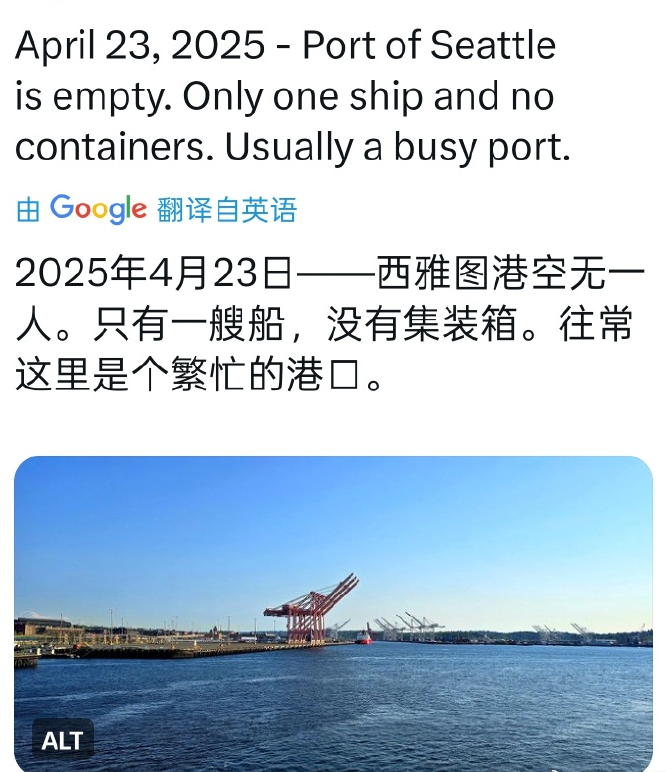
- April 2–26, 2025: Walmart’s inventory dwindled rapidly. By April 26, the retailer urgently requested suppliers to resume shipments, abandoning demands for tariff absorption. Analysts estimate U.S. retailers’ average inventory lasts 1–1.5 months, and Walmart’s scramble confirmed this vulnerability.
 Empty shelves in a Walmart store during the tariff crisis.
Empty shelves in a Walmart store during the tariff crisis.
3. Why Walmart Couldn’t Replace Chinese Suppliers
A. The Myth of Easy Alternatives
- Theoretical vs. Reality: While Mexico, Vietnam, or India could theoretically produce low-cost goods, building factories, training workers, and scaling production would take 3–5 years—far exceeding Walmart’s urgent timeline.
- Supply Chain Complexity: Walmart imports two-thirds of its U.S. products domestically but relies heavily on China and Mexico for the remaining third. Replacing Chinese suppliers would disrupt intricate logistics networks.
B. The Cost of Empty Shelves
- Fixed Costs vs. Lost Sales: Retailers like Walmart face massive fixed costs (e.g., labor, warehouses). Empty shelves mean lost revenue but unchanged expenses, risking financial collapse.
- Customer Loyalty at Stake: Shoppers expect one-stop convenience. Missing product categories drive customers to competitors, eroding market share long-term.
 Shoppers in a Walmart store rely on the convenience of one-stop shopping.
Shoppers in a Walmart store rely on the convenience of one-stop shopping.
4. Behind the Scenes: Secret Tariff Discounts
A. Closed-Door Negotiations
- April 21, 2025: Walmart’s CEO joined other retail leaders in a private White House meeting. While details remain confidential, experts speculate Trump granted tariff discounts on “essential goods” to avoid public outrage over price hikes.
B. Hidden Tariff Rates
- Estimated 20–30%: Though unconfirmed, U.S. retailers’ price increases align with this range. Walmart likely pays far below the 145% headline rate but still faces significant cost pressures.
 Closed-door negotiations at the White House revealed potential tariff discounts for essential goods.
Closed-door negotiations at the White House revealed potential tariff discounts for essential goods.
5. China’s Preparedness vs. U.S. Overconfidence
A. China’s Long-Term Strategy
- Diversifying Imports: For over a decade, China reduced reliance on U.S. goods. Example: By investing in Brazil’s soybean industry, China seamlessly shifted orders during the 2018–2024 trade war, avoiding food shortages.
- Industrial Flexibility: China’s vast manufacturing ecosystem allows rapid shifts in production, while U.S. dependence on Chinese factories limits alternatives.
B. America’s Lack of Contingency Plans
- No Replacement Infrastructure: The U.S. assumed market forces would magically create new suppliers. However, building factories and training workers requires years—not months.
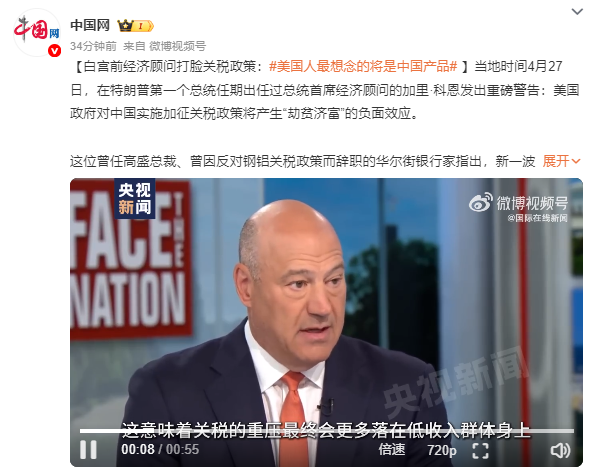
- Regressive Tariff Impact: Low-income households suffer most, as tariffs disproportionately hit essentials like clothing and toys. Former Trump advisor Gary Cohn warned of this “hidden tax on the poor”.
 China’s vast manufacturing ecosystem allows rapid shifts in production.
China’s vast manufacturing ecosystem allows rapid shifts in production.
6. Lessons from Walmart’s Crisis
A. Supply Chain Resilience is Fragile
- Lean Inventories, High Risks: Modern retailers optimize inventory to cut costs, leaving little buffer for disruptions. Walmart’s 20-day collapse highlights this fragility.
B. The Power of “Material Over Money”
- Goods Trump Currency: While money can buy goods in stable times, shortages expose the irreplaceable value of physical products. China’s manufacturing dominance gives it leverage despite lower trade volumes.
C. Political Short-Termism vs. Economic Reality
- Tariffs as Political Theater: Trump’s tariffs aimed to signal strength but ignored supply chain realities. Secret discounts for retailers reveal policy contradictions.
 Supply chain resilience is crucial for maintaining inventory during disruptions.
Supply chain resilience is crucial for maintaining inventory during disruptions.
7. The Road Ahead: Implications for Global Trade
A. Retailers’ New Playbook
- Stockpiling Essentials: Companies may increase safety stocks, despite higher costs.
- Supplier Diversification: Retailers will slowly explore alternatives, but full decoupling remains unlikely.
B. Consumer Impact
- Persistent Price Hikes: Even with tariff discounts, U.S. consumers face 20–30% higher prices on everyday items. Inflation could strain household budgets, especially for low-income families.
C. Geopolitical Uncertainty
- Trade War Escalation Risks: With China refusing negotiations, prolonged tariffs threaten global stability. Retailers like Walmart will remain caught in the crossfire.
8. Conclusion: A Wake-Up Call for Global Supply Chains
Walmart’s 20-day struggle underscores a harsh truth: modern economies rely on seamless global trade. Tariffs designed to punish China instead exposed U.S. vulnerabilities, from fragile supply chains to political shortsightedness.
For Walmart and other retailers, survival now hinges on balancing cost pressures with customer trust—a lesson the broader economy must heed.
